C++虚继承原理--虚表指针的实现
1、编写具体实现的代码
2、#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Animal{
private:
int age;
// 主要验证类的组织存储结构,虚表指针第一个位置存储
virtual void showsAnimal(){
cout<<"this is animal class"<<endl;
}
public:
void show(){
cout<<"animal show"<<endl;
}
virtual void run(){
cout<<"animal run one"<<endl;
}
// 无意中输入,竟然没有报错
virtual void fun(){
cout<<"animal fun two"<<endl;
}
};
class Dog:public Animal{
public:
void fun(){
cout<<"dog fun"<<endl;
}
};
class Cat:public Animal{
public:
void fun(){
cout<<"cat fun"<<endl;
}
};
int main(){
Animal aa;
cout<<"size of : aa -->"<<sizeof aa<<endl; // 虚表指针的存在使得对象多了四字节
aa.run(); // 无意之中的写了两个虚函数,竟然没有出错
Animal ab;
// C++对输出的封装,必须使用强转一下才可以输出地址
cout<<"obj first four bytes of content : aa --> "<<hex<<*(int *)&aa<<endl;
cout<<"obj first four bytes of content : ab --> "<<hex<<*(int *)&ab<<endl;
cout<<"obj first four bytes of content : aa --> "<<hex<<*(int *)&aa<<endl;
// 通过对以上的结果可以看出一个类的不同对象的虚表指针的地址是一样的
int *pa=reinterpret_cast<int *>(&aa); // 取对象 aa 的地址,同时转换为int类型的指针
cout<<"obj first four bytes of content : aa --> "<<hex<<*pa<<endl;
cout<<"obj addr : aa--> "<<hex<<pa<<endl;
pa=reinterpret_cast<int *>(&ab);
cout<<"obj first four bytes of content : ab --> "<<hex<<*pa<<endl;
cout<<"obj addr : ab --> "<<hex<<pa<<endl;
int funs=*(int*)*pa; // 此时对象是ab
cout<<"obj first four bytes of Virtual table : ab --> "<<hex<<funs<<endl;
cout<<"obj first virtual fun this must cout this is a animal class : ab --> ";
((void(*)())(funs))(); // 将funs转化为void类型的无参数的函数,要和第一个虚函数对应
// 从这里也可以看出,对类的private变量的限制主要是通过编译器限制的
// 如果骗过编译器,一样可以访问类的private变量
Dog mydog;
pa=reinterpret_cast<int *>(&mydog);
funs=*((int*) *(int*)(&mydog)); // 此时对象是mydog
cout<<"obj first four bytes of content : mydog --> "<<hex<<*pa<<endl;
cout<<"obj first virtual fun this must cout this is a animal class : mydog --> ";
((void(*)())(funs))(); // 将funs转化为void类型的无参数的函数,要和第一个虚函数对应
// 从这里也可以看出子类本没有函数showsAnimal,但是也有此函数
//以下试验类的多肽的表现
Dog dog,dog1;
pa=reinterpret_cast<int *>(&dog);
cout<<"obj addr : dog --> "<<hex<<*pa<<endl;
pa=reinterpret_cast<int *>(&dog1);
cout<<"obj addr : dog1 --> "<<hex<<*pa<<endl;
Cat cat;
Animal *pdog=&dog;
pdog=&dog;
pdog->fun();
memcpy(&dog,&cat,sizeof(int)); // 内存拷贝函数
pdog=&dog; // 这里本应该是dog的输出,但是拷贝内存以后,
// 变为cat的输出,从这里也可以看出,C++的多肽的实现是基于虚表指针实现的
pdog->fun();
return 0;
}
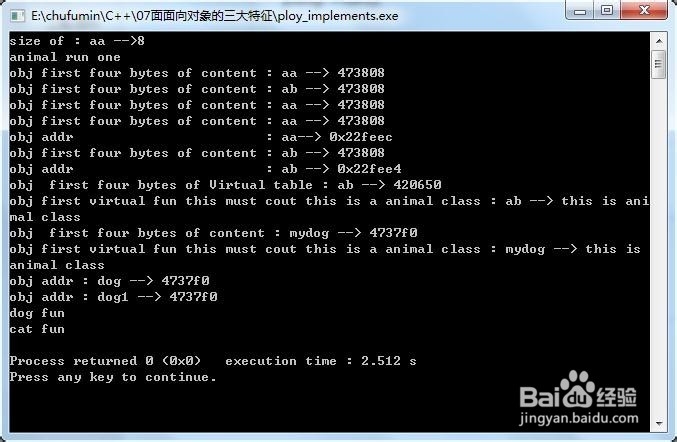
3、结果如下:
注意结果的对比