python中numpy的初始化及索引
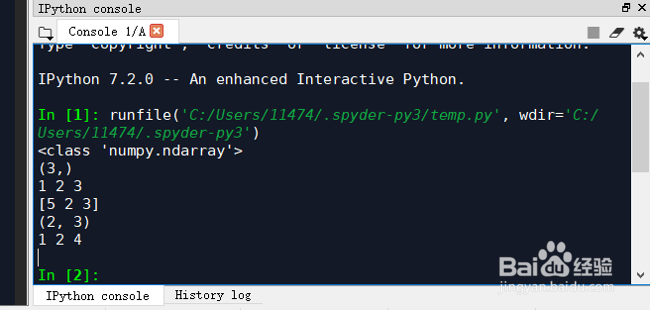
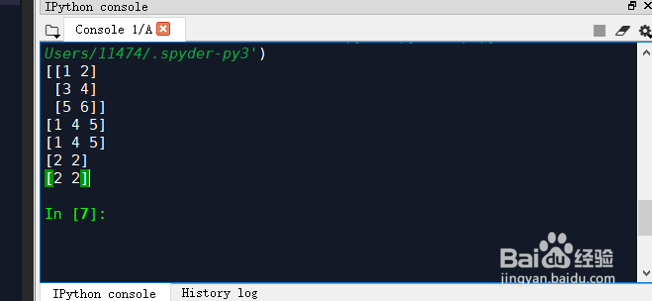
1、list初始化:我们可以通过python内置的list容器初始化numpy数组。举个例子:import numpy as npa = np.array([1, 2, 3]) # Create a rank 1 arrayprint(type(a)) # Prints "<class 'numpy.ndarray'>"print(a.shape) # Prints "(3,)"print(a[0], a[1], a[2]) # Prints "1 2 3"a[0] = 5 # Change an element of the arrayprint(a) # Prints "[5, 2, 3]"b = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) # Create a rank 2 arrayprint(b.shape) # Prints "(2, 3)"print(b[0, 0], b[0, 1], b[1, 0]) # Prints "1 2 4"
2、输出如下:<class 'numpy.ndarray'>(3,)1 2 3[5 2 3](2, 3)1 2 4
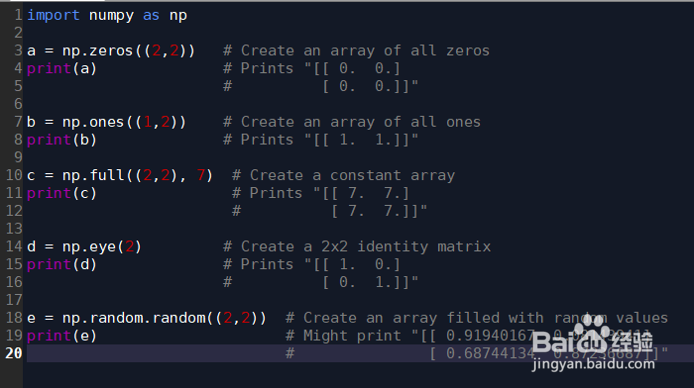
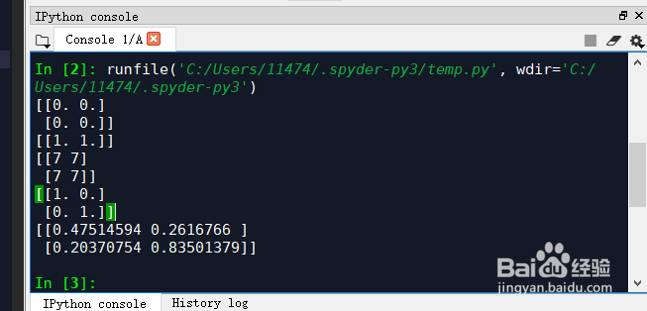
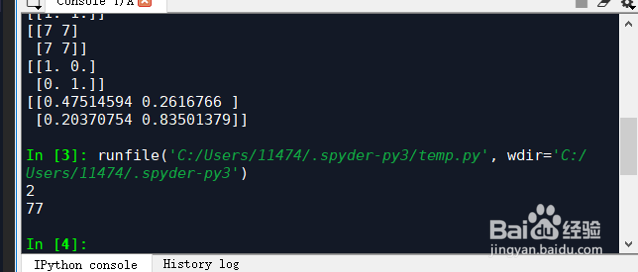
3、初始化方法:numpy也提供了很多函数来初始化numpy数组。举个例子:import numpy as npa = np.zeros((2,2)) # Create an array of all zerosprint(a) # Prints "[[ 0. 0.] # [ 0. 0.]]"b = np.ones((1,2)) # Create an array of all onesprint(b) # Prints "[[ 1. 1.]]"c = np.full((2,2), 7) # Create a constant arrayprint(c) # Prints "[[ 7. 7.] # [ 7. 7.]]"d = np.eye(2) # Create a 2x2 identity matrixprint(d) # Prints "[[ 1. 0.] # [ 0. 1.]]"e = np.random.random((2,2)) # Create an array filled with random valuesprint(e) # Might print "[[ 0.91940167 0.08143941] # [ 0.68744134 0.87236687]]"
4、输出结果:[[0. 0.][0. 0.]][[1. 1.]][[7 7][7 7]][[1. 0.][0. 1.]][[0.47514594 0.2616766 ][0.20370754 0.83501379]]
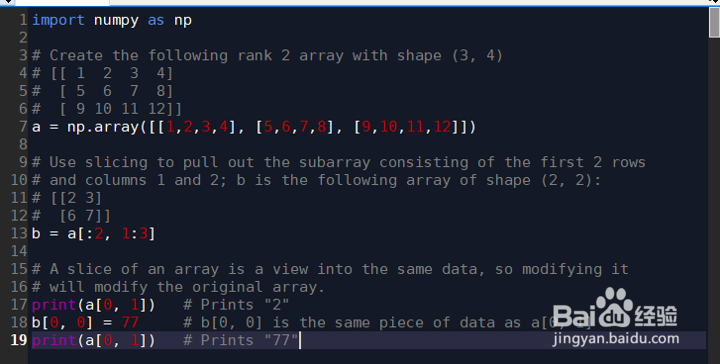
5、索引:numpy提供了许多方法为数组元素进行定位索引。举个例子:import numpy as np# Create the following rank 2 array with shape (3, 4)# [[ 1 2 3 4]# [ 5 6 7 8]# [ 9 10 11 12]]a = np.array([[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8], [9,10,11,12]])# Use slicing to pull out the subarray consisting of the first 2 rows# and columns 1 and 2; b is the following array of shape (2, 2):# [[2 3]# [6 7]]b = a[:2, 1:3]# A slice of an array is a view into the same data, so modifying it# will modify the original array.print(a[0, 1]) # Prints "2"b[0, 0] = 77 # b[0, 0] is the same piece of data as a[0, 1]print(a[0, 1]) # Prints "77"
6、输出结果:277
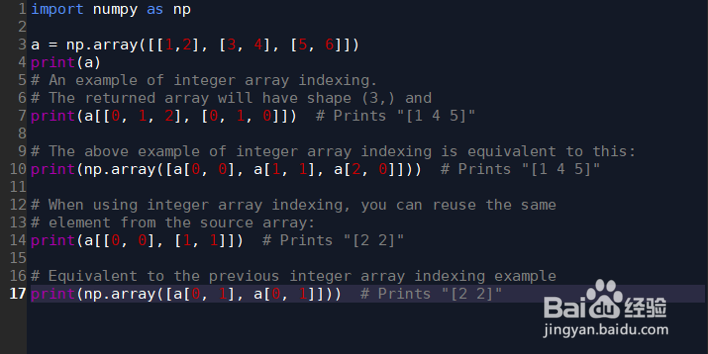
7、整数索引:艘绒庳焰numpy提供了一些整数索引的方式,可以对矩阵中特定几个元素进行操作。举个例子:import numpy as np锾攒揉敫a = np.array([[1,2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])print(a)# An example of integer array indexing.# The returned array will have shape (3,) andprint(a[[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 0]]) # Prints "[1 4 5]"# The above example of integer array indexing is equivalent to this:print(np.array([a[0, 0], a[1, 1], a[2, 0]])) # Prints "[1 4 5]"# When using integer array indexing, you can reuse the same# element from the source array:print(a[[0, 0], [1, 1]]) # Prints "[2 2]"# Equivalent to the previous integer array indexing exampleprint(np.array([a[0, 1], a[0, 1]])) # Prints "[2 2]"
8、运行结果:[[1 2][3 4][5 6]][1 4 5][1 4 5][2 2][2 2]
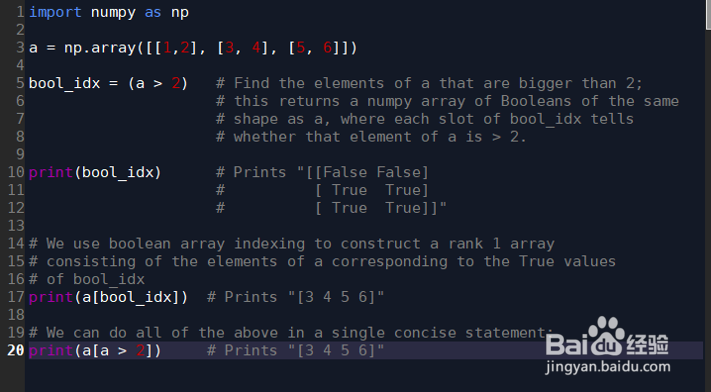
9、布尔数组索引:可以通过布尔数组索引的方式谀薜频扰得到想要得到的数组。举个例子:import numpy as npa = np.array([[1,2], [3, 4], [5, 6]柯计瓤绘])bool_idx = (a > 2) # Find the elements of a that are bigger than 2; # this returns a numpy array of Booleans of the same # shape as a, where each slot of bool_idx tells # whether that element of a is > 2.print(bool_idx) # Prints "[[False False] # [ True True] # [ True True]]"# We use boolean array indexing to construct a rank 1 array# consisting of the elements of a corresponding to the True values# of bool_idxprint(a[bool_idx]) # Prints "[3 4 5 6]"# We can do all of the above in a single concise statement:print(a[a > 2]) # Prints "[3 4 5 6]"
10、输出结果:[[False False][ True True][ True True]][3 4 5 6][3 4 5 6]