如何用PYTHON制作剪刀石头布游戏
1、打开PYTHON,新建一个空白的PYTHON文档。
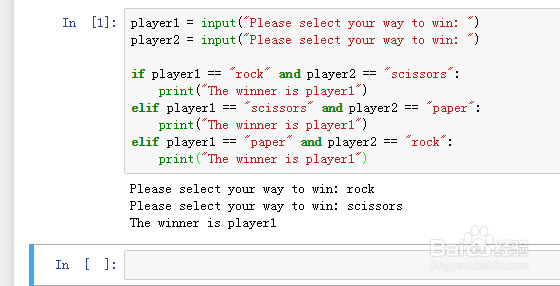
2、player1 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
player2 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
if player1 == "rock" and player2 == "scissors":
print("The winner is player1")
elif player1 == "scissors" and player2 == "paper":
print("The winner is player1")
elif player1 == "paper" and player2 == "rock":
print("The winner is player1")
我们可以让用户输入选择,然后每个条件这样去判断,但是这样很容易遗漏条件,而且会很复杂。
3、player1 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
player2 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
if player1 == "rock" and player2 == "scissors":
print("The winner is player1")
elif player1 == "scissors" and player2 == "paper":
print("The winner is player1")
elif player1 == "paper" and player2 == "rock":
print("The winner is player1")
换了另一个输入就可以看出有问题了。

4、player1 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
player2 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
if player1 == "rock":
if player2 == "scissors":
print("The winner is player1")
else:
print("The winner is player2")
elif player1 == "scissors":
if player2 == "rock":
print("The winner is player2")
else:
print("The winner is player1")
elif player1 == "paper":
if player2 == "rock":
print("The winner is player1")
else:
print("The winner is player2")
其实可以设置一下条件,让条件更加合理一些,有层次感。

5、rules = {"rock": {"scissors": "wins",
"paper": "loses"},
"scissors": {"rock": "loses",
"paper": "wins"},
"paper": {"rock": "wins",
"scissors": "loses"}}
player1 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
player2 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
print("The player1 " + rules[player1][player2])
我们也可以用字典来定义规则,字典里面还可以添加字典,这样直接导出结果。

6、rules = {"rock": {"scissors": "wins",
"paper": "loses"},
"scissors": {"rock": "loses",
"paper": "wins"},
"paper": {"rock": "wins",
"scissors": "loses"}}
player1 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
player2 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
def who_wins(a, b):
if a == b:
print("Draw")
for i in rules:
if a == i and b == rules[i]:
print("The player1 " + rules[player1][player2])
who_wins(player1, player2)
不要忘了我们还可以用FUNCTION来代替繁杂的IF语句。

7、import random
player1 = input("Please select your way to win: ")
def who_wins(choice):
options = ["rock", "scissors", "paper"]
player2 = random.choice(options)
print("player2 is using {}.".format(player2))
if player1 == "rock":
if player2 == "scissors":
print("The winner is player1")
else:
print("The winner is player2")
elif player1 == "scissors":
if player2 == "rock":
print("The winner is player2")
else:
print("The winner is player1")
elif player1 == "paper":
if player2 == "rock":
print("The winner is player1")
else:
print("The winner is player2")
elif player1 == player2:
return("Draw")
who_wins(player1)
我们还可以用RANDOM来随机玩家输入的选项,这样会更加有趣。
