Linux中使用sort对文档中的内容进行排序
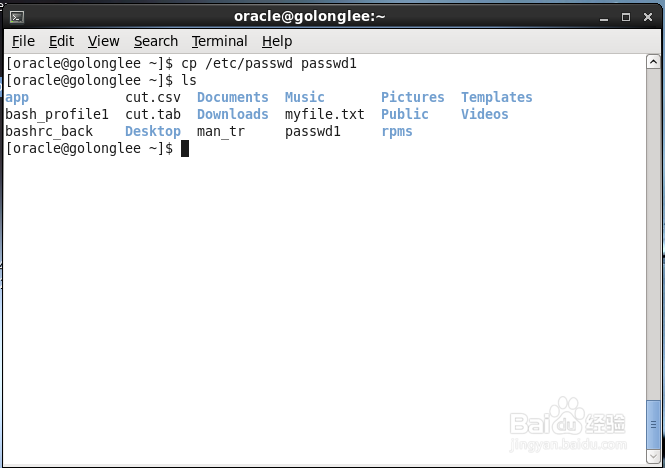
1、复制一个passwd文档,并查看passwd文档内容
[lele@Oracle ~]$ cp /etc/passwd passwd.1
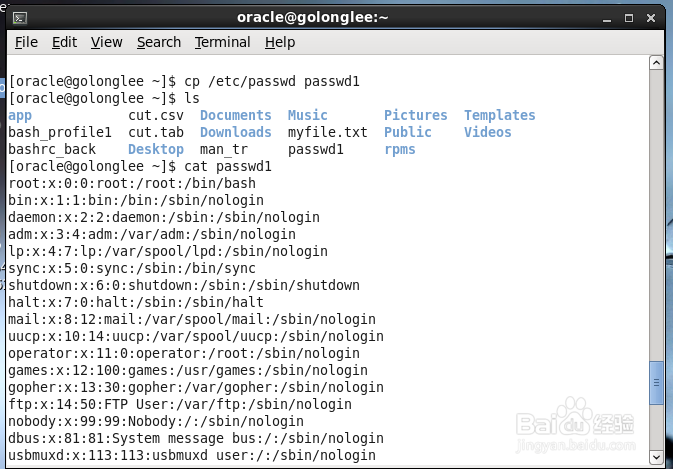
[lele@Oracle ~]$ cat passwd.1
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
2、用cat命令查看该文件内容
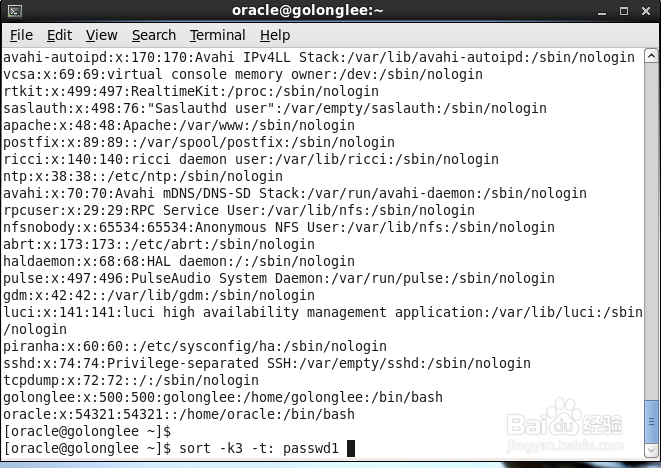
3、对该文档的第3段进行排序,所以使用第3个栏位区间,也就是-k3参数,因为每段使用冒号:分隔,所以使用-t:参数,因为要对passwd文档中的内容进行排序,所以完整的命令是如下
sort -k3 -t: passwd
结果如下
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
usbmuxd:x:113:113:usbmuxd user:/:/sbin/nologin
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
gopher:x:13:30:gopher:/var/gopher:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
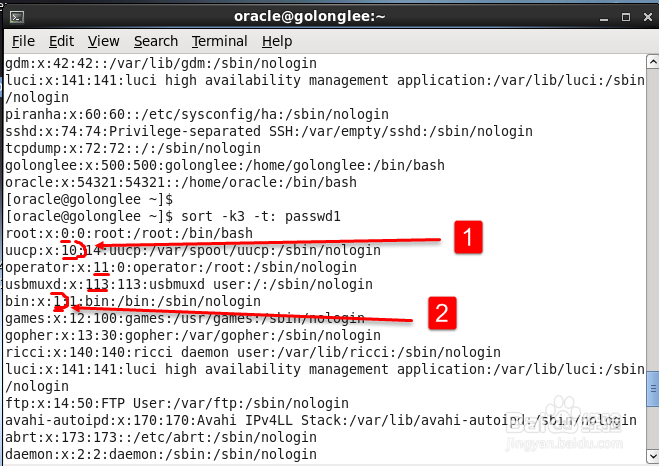
这里发现第3列没有按数字进行排序,而是以字符进行排序,没有达到预期
4、这里看到没有按0,1,2这种顺序排,那说明是按字符顺序排序的,不是我们的目标
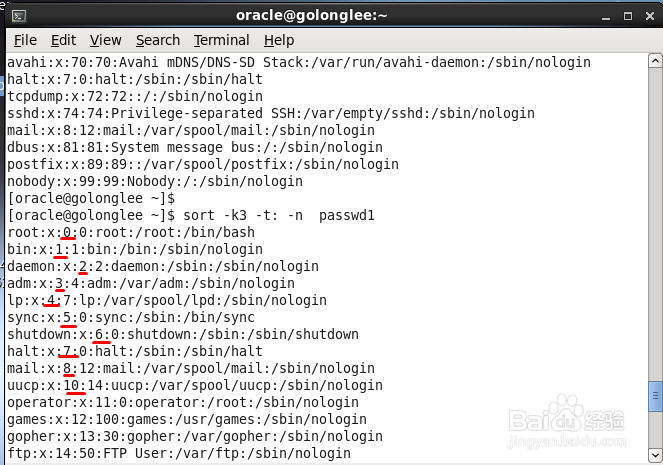
5、第3段进行排序,用数值顺序进行排序,要使用-n参数,命令如下
sort -k3 -t: -n passwd
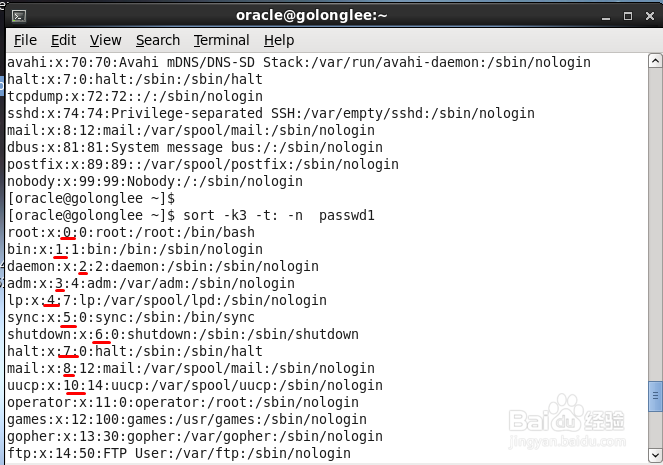
6、我们从图片中确认一下,看到确实是按照第3个字段按数字顺序排序的,很好
7、如果以上经验帮到您,麻烦在左下角给点个赞,谢谢!

8、如果我们要使用第3段进行排序,用数值顺序进行排序,也就是要使用-n参数,完整的命令如下:
sort -t: -k3 -n passwd
结果如下
[lele@Oracle ~]$ sort -t: -k3 -n passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
这里看到结果是按第三列按数值大小进行排序的
9、下面是sort命令的reference book
SORT(1) User Commands SORT(1)
NAME
sort - sort lines of text files
SYNOPSIS
sort [OPTION]... [FILE]...
sort [OPTION]... --files0-from=F
DESCRIPTION
Write sorted concatenation of all FILE(s) to standard output.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options
too. Ordering options:
-b, --ignore-leading-blanks
ignore leading blanks
-d, --dictionary-order
consider only blanks and alphanumeric characters
-f, --ignore-case
fold lower case to upper case characters
-g, --general-numeric-sort
compare according to general numerical value
-i, --ignore-nonprinting
consider only printable characters
-M, --month-sort
compare (unknown) < ‘JAN’ < ... < ‘DEC’
-h, --human-numeric-sort
compare human readable numbers (e.g., 2K 1G)
-n, --numeric-sort
compare according to string numerical value
-R, --random-sort
sort by random hash of keys
--random-source=FILE
get random bytes from FILE
-r, --reverse
reverse the result of comparisons
--sort=WORD
sort according to WORD: general-numeric -g, human-numeric -h,
month -M, numeric -n, random -R, version -V
-V, --version-sort
natural sort of (version) numbers within text
Other options:
--batch-size=NMERGE
merge at most NMERGE inputs at once; for more use temp files
-c, --check, --check=diagnose-first
check for sorted input; do not sort
-C, --check=quiet, --check=silent
like -c, but do not report first bad line
--compress-program=PROG
compress temporaries with PROG; decompress them with PROG -d
--files0-from=F
read input from the files specified by NUL-terminated names in
file F; If F is - then read names from standard input
-k, --key=POS1[,POS2]
start a key at POS1 (origin 1), end it at POS2 (default end of
line)
-m, --merge
merge already sorted files; do not sort
-o, --output=FILE
write result to FILE instead of standard output
-s, --stable
stabilize sort by disabling last-resort comparison
-S, --buffer-size=SIZE
use SIZE for main memory buffer
-t, --field-separator=SEP
use SEP instead of non-blank to blank transition
-T, --temporary-directory=DIR
use DIR for temporaries, not $TMPDIR or /tmp; multiple options
specify multiple directories
-u, --unique
with -c, check for strict ordering; without -c, output only the
first of an equal run
-z, --zero-terminated
end lines with 0 byte, not newline
--help display this help and exit
--version
output version information and exit
POS is F[.C][OPTS], where F is the field number and C the character
position in the field; both are origin 1. If neither -t nor -b is in
effect, characters in a field are counted from the beginning of the
preceding whitespace. OPTS is one or more single-letter ordering
options, which override global ordering options for that key. If no
key is given, use the entire line as the key.
SIZE may be followed by the following multiplicative suffixes: % 1% of
memory, b 1, K 1024 (default), and so on for M, G, T, P, E, Z, Y.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
*** WARNING *** The locale specified by the environment affects sort
order. Set LC_ALL=C to get the traditional sort order that uses native
byte values.
AUTHOR
Written by Mike Haertel and Paul Eggert.
REPORTING BUGS
Report sort bugs to bug-coreutils@gnu.org
GNU coreutils home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>
Report sort translation bugs to <http://translationproject.org/team/>
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2010 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU
GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
SEE ALSO
The full documentation for sort is maintained as a Texinfo manual. If
the info and sort programs are properly installed at your site, the
command
info coreutils 'sort invocation'
should give you access to the complete manual.