如何在PYTHON中导入和测试模块
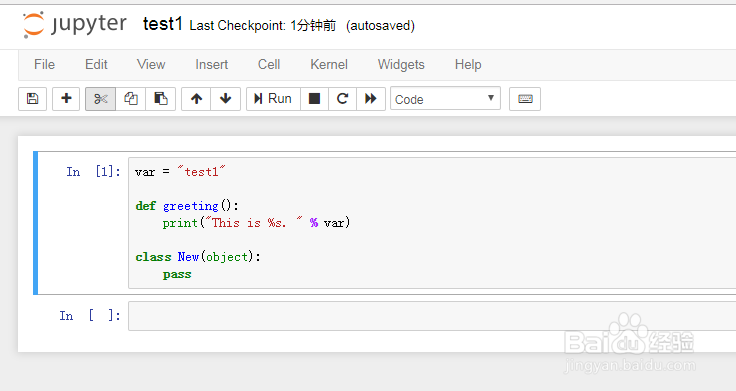
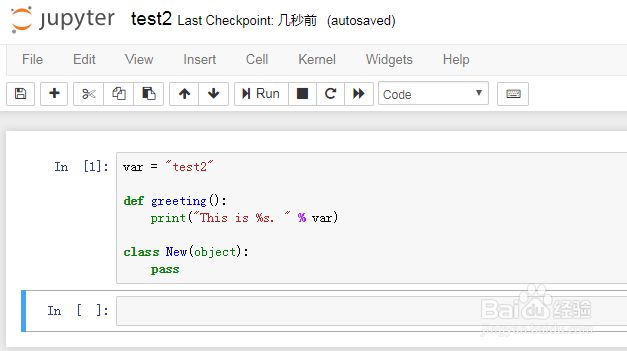
1、定义两个PYTHON文件,注意要保存为py后缀的文件。
2、import test1import test2这个时候就可以直接导入了。如果后缀是ipynb则不能直接导入。
3、import test1import test2test1.greeting()test2.greeting()导入以后就可以这样来把函数调用出来。
4、import test1 as oneimport test2 as twoone.greeting()two.greeting()为了方便个人书写,自己可以定义导入模块的名字。
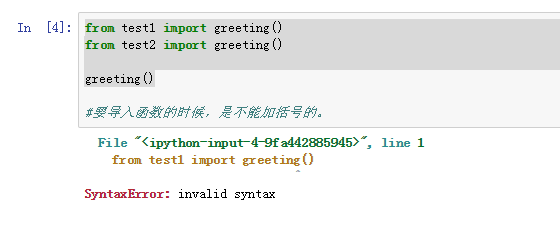
5、from test1 import greeting()from test2 import greeting()greeting()要导入函数的时候,是不能加括号的。
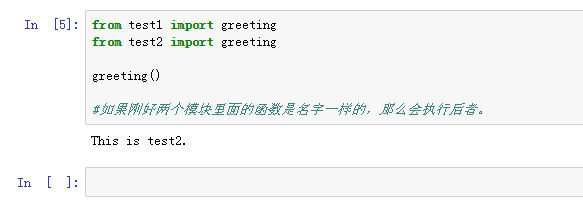
6、from te衡痕贤伎st1 import greetingfrom test2 import greetinggreeting()如果刚好两个模块里面的函数是名字一样的,那么会执行后者。
7、from test1 import *greeting()new = New()如果用*可以全部导入,但是这种很少用,也不推荐。
8、import test1print(test1.__file__)用__file__可以查看导入模块的位置。首先会搜索导入当前目录的,没有才会搜索系统的模块,所以不要重名。
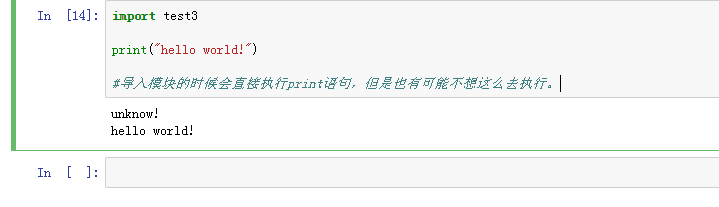
9、import test3print("hello world!")导入模块的时候会直接执行print语句,但是也有可能不想这么去执行。
10、print("unkno嘛术铹砾w!")print(__name__)var = __name__type(var)如果输入__name__会直接返回__main__,是一个字符串。
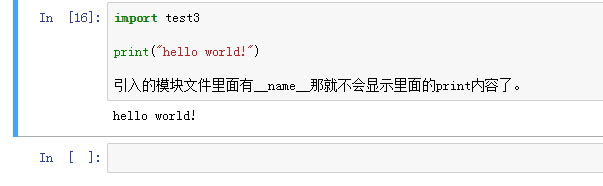
11、if __name_娄多骋能_ == "__main": print(__name__) print("hellooooo") 我们可以多加一个判断。import test3print("hello world!")引入的模块文件里面有__name__那就不会显示里面的print内容了。